CNN Básica con Pytorch
Escrito por
6 minutos de lectura
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
imgUrl = "../../assets/5.CNN-Layers-Feature-Visualization/"
tesla_img = cv2.imread(imgUrl + "tesla.jpg")
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(tesla_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Normalize, rescale entries to lie in [0, 1]
gray_img = gray_img.astype("float32")/255
plt.imshow(gray_img, cmap="gray")
plt.show()

Definir y visualizar filtros
filter_vals = np.array([[-1, -1, 1, 1], [-1, -1, 1, 1], [-1, -1, 1, 1], [-1, -1, 1, 1]])
# Define four filters
filter_1 = filter_vals
filter_2 = -filter_1
filter_3 = filter_1.T
filter_4 = -filter_3
filters = np.array([filter_1, filter_2, filter_3, filter_4])
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for i in range(4):
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
ax.imshow(filters[i], cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('Filter %s' % str(i+1))
width, height = filters[i].shape
for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
ax.annotate(str(filters[i][x][y]), xy=(y,x),
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
color='white' if filters[i][x][y]<0 else 'black')

Definir una convolutional layer
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# Initializes the weights of the convolutional layer to be the weights of the 4 defined filters
k_height, k_width = weight.shape[2:]
# Assumes there are 4 grayscale filters
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=(k_height, k_width), bias=False)
self.conv.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(weight)
def forward(self, x):
# Calculates the output of a convolutional layer
conv_x = self.conv(x)
activated_x = F.relu(conv_x)
return conv_x, activated_x
# Instantiate the model ad set the weights
weight = torch.from_numpy(filters).unsqueeze(1).type(torch.FloatTensor)
model = Net(weight)
print(model)
Net(
(conv): Conv2d(1, 4, kernel_size=(4, 4), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
)
Visualizar el output de cada filtro
def visualize_layer(layer, n_filters=4):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
for i in range(n_filters):
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, n_filters, i+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
# Grab layer outputs
ax.imshow(np.squeeze(layer[0,i].data.numpy()), cmap="gray")
ax.set_title('Output %s' % str(i+1))
# Plot original image
plt.imshow(gray_img, cmap='gray')
# Visualize all filters
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1.5, bottom=0.8, top=1, hspace=0.05, wspace=0.05)
for i in range(4):
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
ax.imshow(filters[i], cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('Filter %s' % str(i+1))
# Convert the image into an input Tensor
gray_img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(gray_img).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(1)
# Get the convolutional layer (pre and post activation)
conv_layer, activated_layer = model(gray_img_tensor)
visualize_layer(conv_layer)


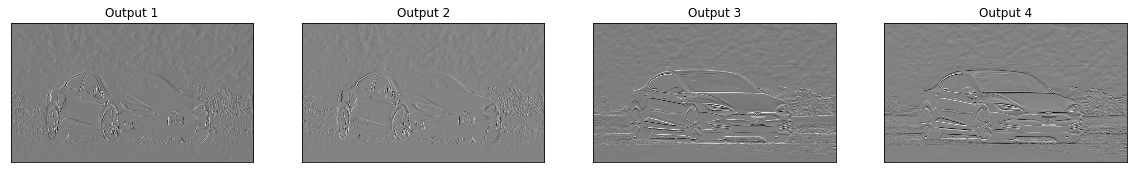
# Visualize the output of an activated conv layer
visualize_layer(activated_layer)

¿Quieres contactar conmigo?
Reporta un bug
Para cualquier error en la web o en la escritura, porfavor abre un issue en Github.
GithubMándame un mensaje
Siéntete libre de mandarme un tweet con cualquier recomendación o pregunta.
Twitter